Eagle Animal Hospital
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery for dogs
Minimally invasive abdominal scoping procedure
Quicker recovery times
Less pain and discomfort post-surgery and during recovery
Smaller incisions when compared to traditional procedures
Can clearly see internal abdominal structures without large incisions
Exploratory surgery with less pain
Involves the use of a general anesthesia
An optimal alternative procedure for spaying female dogs
Quicker surgery times than traditional procedures
Reduced risk of post-op infection and other complications with wound healing
Can detect health diseases such as cancer or abnormal growth
LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY AT KANSAS CITY’S TOP RATED LOCAL® ANIMAL HOSPITAL
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure of the belly allowing veterinarians to explore the abdomen and abdominal organs in dogs. Often referred to as ‘keyhole surgery,’ this type of surgical procedure is typically performed for specific reasons, such as a laparoscopic spay as a minimally invasive alternative to traditional spay procedures in female dogs. Your veterinarian may also recommend an exploratory laparoscopy to view the abdomen in order to detect diseases, such as stomach cancer and other abnormalities. Unlike traditional scalpel-based surgeries, a laparoscopy procedure involves making a small incision to allow a small tubular scope with a tiny camera (laparoscope) to enter the abdomen giving your pet surgeon a close-up view of the abdomen. For surgical procedures, another small incision can then be made to perform the actual surgery, with the scope giving your pet surgeon a clear view of the abdominal surgical site, allowing for quicker, more precise surgeries. Laparoscopy can be performed through a few small incisions, with reduced tissue damage, less pain, and ultimately, a quicker recovery time for your pet.
UNDERSTANDING A LAPAROSCOPIC PROCEDURE
Laparoscopic surgery is a common, minimally invasive pet surgery that is similar to a gallbladder removal in humans. This procedure can be used as a scoping mechanism to investigate the abdominal cavity, or as a surgical procedure to remove a female dog’s ovaries, to remove a tumor from the stomach, or to prevent bloat (twisting of the stomach). After determining that your pet is a good candidate for laparoscopy, the patient (your pet) will return to our animal hospital to undergo their procedure. Your pet will be given a general anesthesia, meaning they will have to fast for 12-hours prior to their procedure. Once anesthetized, your pet surgeon will begin the abdominal scoping or surgery, depending on the reason for your pet’s procedure. Following the laparoscopy, you dog’s incisions will be sutured. They should wake up with only minor discomfort and typically recover much quicker when compared to other surgeries.
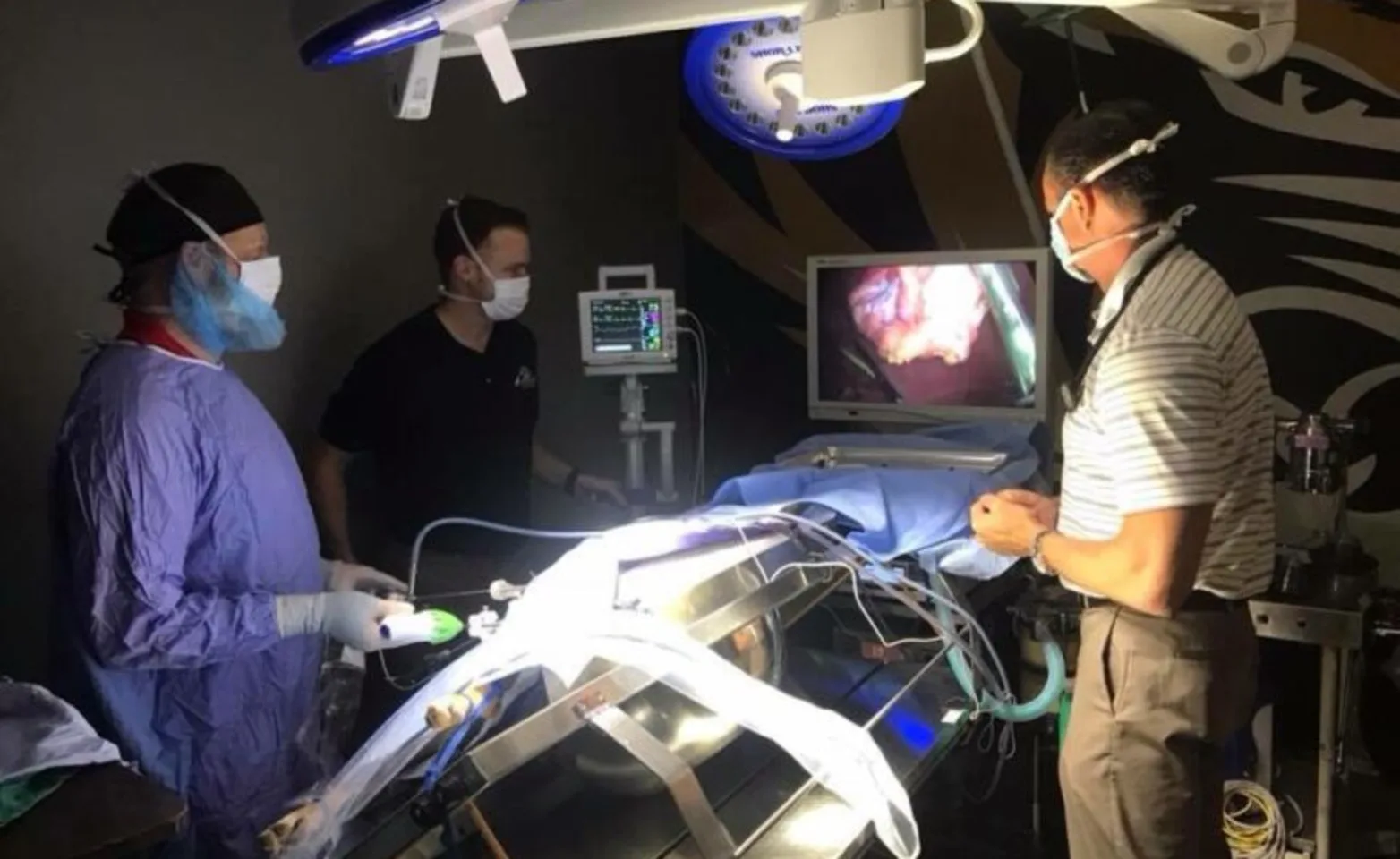
When is a dog a candidate for a Laparoscopic procedure?
Your veterinarian may recommend a laparoscopic procedure for the following reasons:
Minimally invasive exploratory scope to view the abdominal cavity close-up.
Minimally invasive spay procedure to remove a female dog’s ovaries, rather than the entire reproductive system (ovaries and uterus), which is standard practice in traditional spay procedures involving larger incisions and longer recovery times.
To quickly remove a tumor or other abnormal growth with small incisions for less pain and quicker recovery time.
